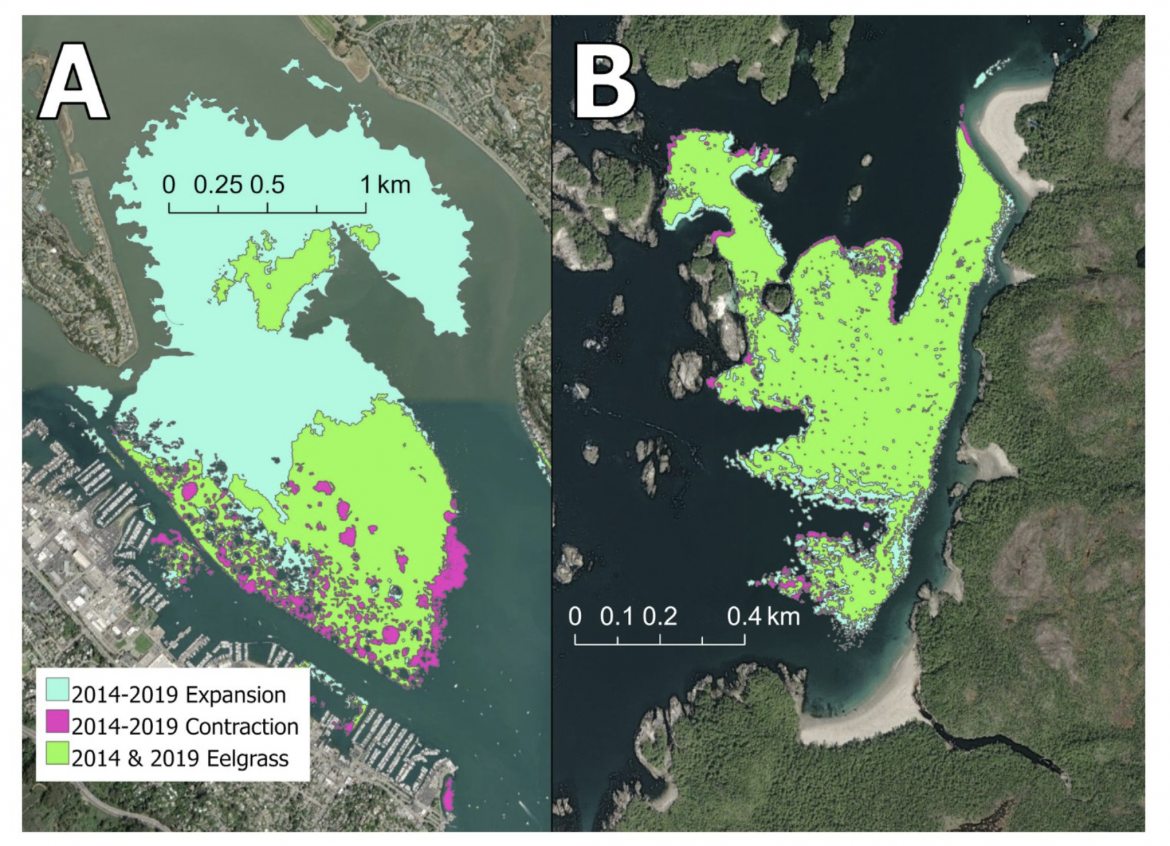
Fig. 6. Greater eelgrass dynamism between 2014 and 2019 in (A) Richardson Bay, CA, compared to (B) Choked Pass, BC. Richardson Bay is exposed to stressors including eutrophication, runoff, heat stress, drought, sedimentation, and scour, whereas these natural and human stressors are less intense at Choked Pass
ABSTRACT
Ecosystems constantly change, yet managers often lack information to move beyond static habitat assumptions. As human impacts and geographic information systems advance, it is important and feasible to quantify past habitat boundary shifts to inform management decisions (e.g. protective perimeters) robust to near-term habitat changes. This is the case in eelgrass (Zostera spp.), an ecosystem engineer that forms dynamic, often protected meadows. Practitioners protect areas to avoid human stress to eelgrass, but they can lack quantitative descriptions of the near-term potential for eelgrass meadows to shift into unprotected areas. Here, we quantified interannual eelgrass meadow boundary shifts within 23 sites spanning 9 decades and 19° latitude. Eelgrass meadow boundaries typically shifted into areas tens of meters away from previous meadow edges, but sometimes much farther. Also, eelgrass meadows often vacated and later recolonized the same areas. By implication, eelgrass protection efforts may be enhanced by considering that presently vacant areas may be inhabited in the future, especially near currently existing meadows. Additionally, eelgrass meadows changed less over time at sites less modified by people within temperate landscapes compared to sites located within human-dominated, warmer, and drought-prone landscapes with limited water turnover. We thus hypothesize that eelgrass meadows change more over time within landscapes exposed to greater stressor regimes because they more frequently or intensely cycle through disturbance and recovery phases. These results inform tactical decisions seeking to mitigate impacts of human activities to eelgrass and underscore the potential synergy of monitoring, research, and adaptive management approaches to protect dynamic habitats.